1. What is FUKOIDAN?
Fucoidan is found in kelp, seaweed, sea mustard, (mozuku) (curly pondweed) and hijiki (Fusiform algae). Koreans and Japanese have been familiar with seaweed for a long time, you can always find this product on their tables. Algae contains many minerals such as calcium, iodine, vitamins and dietary fiber, contains a minimum of calories, and thus contributes to weight loss.
Much research has been done on algae both in America and in Europe, and the research findings deserve special attention. Algae, sea mustard and mozuki have a slimy surface that forms a substance called fukoidan, a type of fiber that is undoubtedly beneficial to health.
2. What is important in seaweed?
First of all, it is seaweed mucus. Algae are classified as brown, red, green and blue-green algae. Kelp is classified as typical seaweed, sea mustard, mozuku, and hijiki; red algae are subdivided into agar-agar and purple algae; blue-green algae are subdivided into spirulina. Like all plants that grow with photosynthesis, the same thing happens with algae. Blue-green algae grow on rocks or cliffs, while green algae grow in shallow waters and therefore get enough light. Brown algae and red algae grow in both shallow and deep seas, respectively, and these plants can undergo photosynthesis with little light. How is fukoidan produced in algae, especially in brown algae, and what is its function?
Fukoydan is secreted like mucus from the algae canal when a leaf or stem is damaged by the flow of water or sand, and thus protects itself from bacterial invasion. In addition, when the algae is exposed to air, fukoidan is released and moisturizes the damaged part.
3. The structure of fukoidan.
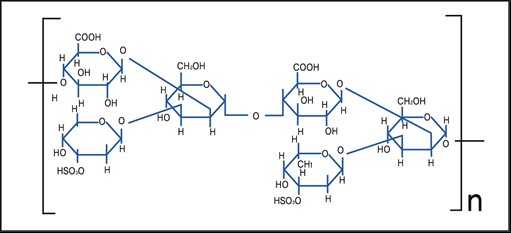
Fucoidan is known to have different molecular weights, chemical structures and functions, depending on the algae from which it is secreted. Usually it has a bond: alpha (1 → 2) L-fucose, the sulfate group is linked to the 4th carbon. L-fucose is known to be the primary sugar in fucoidan, but galactose and uronic acid are the primary sugars.
4. Fukoidan is a polysaccharide.
Fukoidan contains various sugars, namely a heteroatom-polysaccharide. For reference, starch has only one sugar and is called a “homo-polysaccharide. Fukoydan is a kind of proteoglycan and is linked to a protein. Fukoydan is made up of monosaccharides and a sulfate group is linked to each monosaccharide. As stated above, L-fucose is the L-form. monosaccharide and is the main component of fukoidan. Most natural monosaccharides are D-form. In addition to OH, CH3 is often associated with L-fucose. In most cases, natural monosaccharides do not have CH3. The unusual L-form and CH3 have important roles in hetero function -polysaccharides.
Fukoidan is highly anionic, which can be caused by a high density sulfate group (SO-24). A common polysaccharide such as chitosan, the radical anion is below minus 1. Anionic substances are more effective in biological activity related to homeostasis. Proteoglycan, which has a sulfate group, is commonly seen in animals (cockscomb, blood, shark cartilage, skin, etc.). Kelp can also be found in echinoderms such as sea cucumbers, starfish, and sea urchins.
5. Fukoidan has a self-healing effect
Fukoidan is known to induce apoptosis in cancer cells as well as the power of self-healing. Everyone has a natural resistance to disease, which we call “the power of self-healing” or “immunity.” The immune system is weakened with age due to stress or poor nutrition. We know from experience that wounds or bruises heal quickly in young people, and it takes more time in older people This is due to the power of self-healing. As a result, older people are more prone to various diseases. Research results have shown that Fukkoidan is a natural immunity-enhancing product. An experiment was performed with mice fed food mixed with Fukkoidan and it was found that natural killer (NK) cells were highly activated at least twice.
6. Fukoydan leads cancer cells to apoptosis Gly Tech Inc.
(Gly-Tech Inc.), based in Japan, found that fukoidan causes cancer cells to undergo apoptosis, but practically does not affect normal cells, and thus came to the conclusion that fukoidan can be used as an anticancer drug with no side effects. effects. Such results were presented at the 55th General Assembly of the Japan Cancer Association in 1996, and since then, fukoidan has become the subject of study by scientists around the world.